The total solar energy transmittance (or solar factor) g is computed according to DIN 67 507, EN 410 or ISO9050:2003. CODE can handle single, double and triple glazings. A gas like air or Ar has to be used between two panes.
In order to compute g CODE has to use some physical properties of the filling gas. The properties of the gases air, Argon, SF6, Krypton and Xenon have been taken from EN 673 and stored in the database. Please use these materials in your layer stack
g is the sum of the solar direct transmittance τe and the secondary internal heat transfer factor qi. The quantity qi as well as the corresponding quantity qe (the secondary external heat transfer factor) are also available as integral quantities.
g can only be calculated for simulated spectra, not for measured spectra. CODE needs to compute the emissivities from parts of the layer stack. This is not possible in the case of experimental data.
CODE needs to compute the emissivity of the coated glass panes in the far infrared (200 ... 1800 1/cm). Make sure that your optical model is valid in this spectra range. If you do not have optical constants in this spectral range you can still compute g if you know the emissivity of the involved surfaces. In this case, Edit the g quantity in the list of integral quantities. This dialog will open:
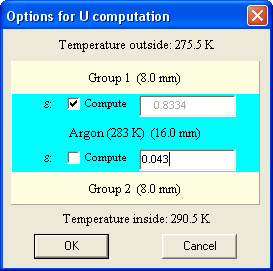
Note that the individual layers are not drawn in the dialog's sketch.
Using the checkboxes at the interfaces you can decide if CODE should compute the emissivity at this interface from the optical model. If the option is unchecked you can type in the emissivity to be used for this interface. If the option is checked CODE will indicate (in gray) the computed value of the emissivity.